In my previous blog post, I introduced you to the Azure MLOps Challenge, a hands-on learning experience that guides you through the creation and deployment of a machine learning model using Azure Machine Learning and GitHub Actions. I also gave you an overview of the main objectives and technologies that you will encounter in the challenge and how they relate to each other.
In this blog post, I will show you how to complete the second module of the challenge, which is to create an Azure Machine Learning job. A job is an execution of a script or a pipeline that performs a machine learning task, such as data preprocessing, model training or model evaluation. A job can run on various compute targets, such as local machines, virtual machines or Kubernetes clusters. A job can also produce outputs such as metrics, logs and artifacts that can be tracked and stored in your workspace.
Here is a brief description of technologies you’ll encounter in this challenge, that weren’t covered in the previous blog/s.
- Compute target: You can use two types of compute targets: compute instances and compute clusters. A compute instance is a single-node VM that you can use as your development environment or as a training or inferencing target for small-scale workloads. A compute cluster is a multi-node cluster of CPU or GPU nodes that you can use as a training or batch inferencing target for high-performance or distributed workloads. You can create and manage both types of compute targets from the Azure Machine Learning Studio, the Azure Machine Leaning SDK, the Azure CLI, or an Azure Resource Manager template.
- Azure Machine Learning CLI v2: is a way to use the Azure Command Line Interface (CLI) to create and manage Azure Machine Learning assets and workflows. The CLI v2 provides commands in the format
az ml <noun> <verb> <options>to perform tasks such as creating a workspace, registering a dataset, submitting a job or deploying a model. The assets or workflows themselves are defined using a YAML file that specifies the configuration and parameters. You can use the CLI v2 to onboard to Azure Machine Learning without the need to learn a specific programming language, to ease deployment and automation, to leverage managed inference deployments, and to reuse components in pipelines.
The goal of this module is to create a Azure Machine Learning job using the CLI that trains a classification model using the python script we created in the previous module. We will use the Azure Machine Learning CLI to create and submit the job, then we will use the Azure Machine Learning studio to monitor and view the job results.
In this blog post, I will walk you through the following steps:
- Create an Azure Machine Learning workspace
- Create a compute target for the job
- Use the training script we created in the first module
- Use the Azure Machine Learning CLI to start a job
- Monitor and view the job results
By the end of this blog post, you will have learned how to create an Azure Machine Learning job using the CLI and how to use it to train a machine learning model. You will also have gained some experience with using the Azure Machine Learning CLI and the Azure Machine Learning Studio.
Let’s get started! 🚀
Challenge 1: Create an Azure Machine Learning job
The Objectives of the second challenge are as follows:
- Define an Azure Machine Learning job in YAML.
- Run an Azure Machine Learning job with the CLI v2.
I won’t go into detail on capabilities, features or installation of the Azure Machine Learning CLI (v2) in this blog however, if you’d like to know more I’d highly recommend is this Microsoft Learn Learning Path:
(https://learn.microsoft.com/en-gb/training/paths/train-models-azure-machine-learning-cli-v2/)
We’ll kick things off by making a new resource group for our ML Workspace, then create the workspace and the compute cluster.
# Create a resource group
az group create --name myResourceGroup --location australiaeast
# Create a workspace
az ml workspace create --resource-group myResourceGroup --name myWorkspace
# Create a compute cluster
az ml compute create --name myCompute --size Standard_DS3_v2 --type AmlCompute --workspace-name myWorkspace --resource-group myResourceGroup
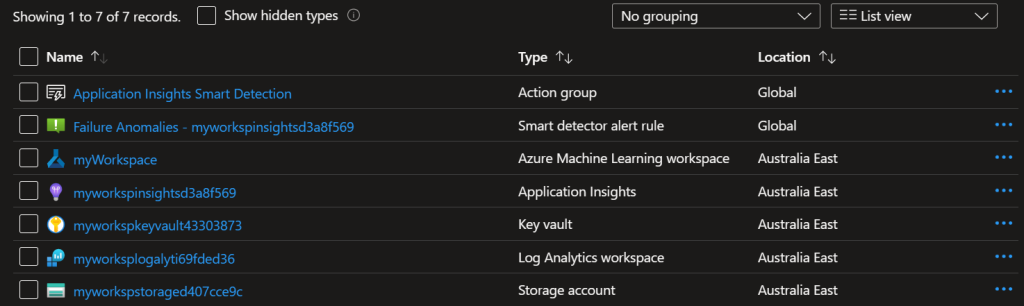
Having a look in the Azure Portal we can see all the resources have been created successfully.
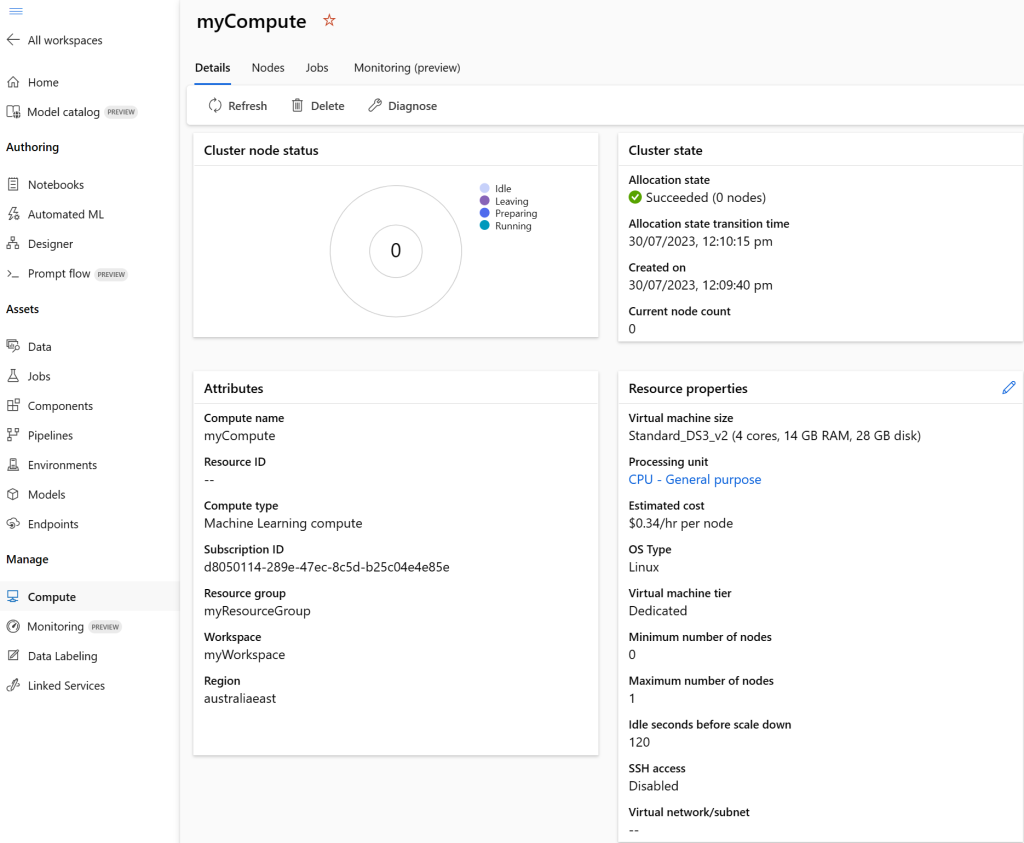
And in Azure Machine Learning Studio the compute cluster is registered and ready to go
Next we’ll create our dataset asset. We’ll create a file named dataset.yml and specify the name and path as specified in the Challange Instructions.
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/asset.schema.json
name: diabetes-dev-folder
version: 1
path: experimentation/data
description: Dataset pointing to diabetes-dev CSV in the repo. Data will be uploaded to default datastore.
Using the CLI (v2), we’ll create a dataset asset in the workspace. Azure Machine Learning will then automatically upload the CSV to the workspace’s default datastore. The default datastore is the storage account that was created together with the workspace.
az ml data create --file dataset.yml --workspace-name myWorkspace --resource-group myResourceGroup
We can see the date asset in Machine Learning Studio
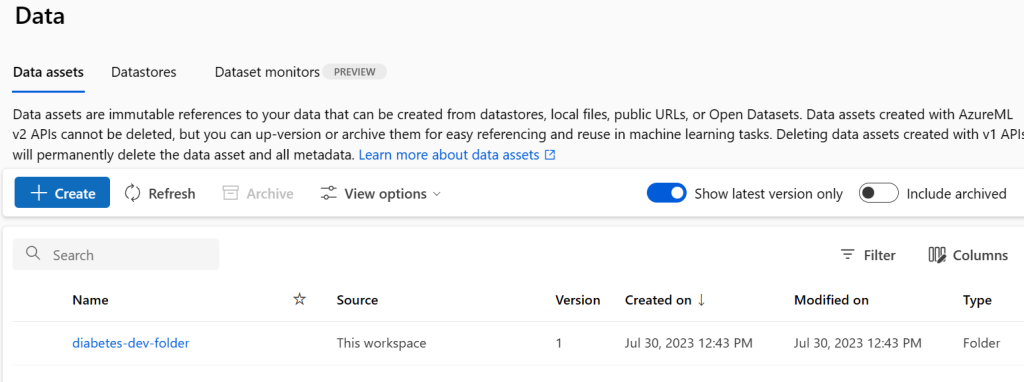
Finally we’ll update job.yml to reference the train.py script created in the previous module and the compute cluster and dataset asset we created in this module.
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/commandJob.schema.json
code: model
command: >-
python train.py
--training_data {inputs.training_data}
--reg_rate {inputs.reg_rate}
inputs:
training_data:
type: uri_folder
path: azureml:diabetes-dev-folder:1
reg_rate: 0.01
environment: azureml:AzureML-sklearn-0.24-ubuntu18.04-py37-cpu@latest
compute: azureml:myCompute
experiment_name: diabetes-classification-experiment
description: Train a classification model to predict diabetes
The following command will create a job using the above yml file.
az ml job create --file src\job.yml --workspace-name myWorkspace --resource-group myResourceGroup
If we quickly jump over the ML Studio we can see the compute cluster starting to spin up.
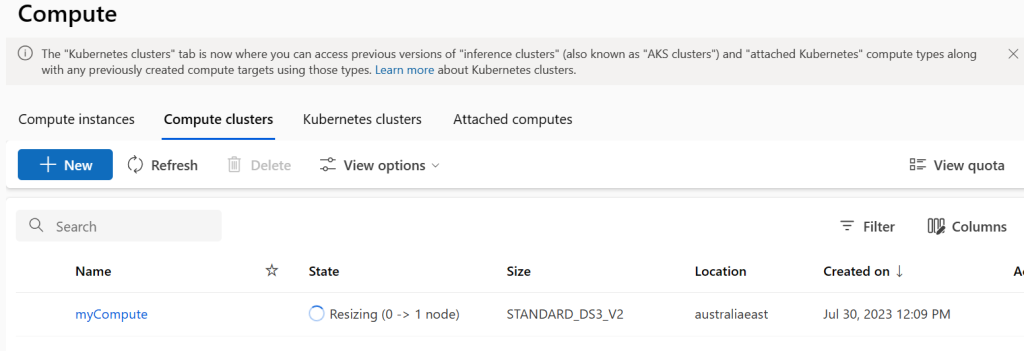
And to close is out we can view the completed job in Azure Machine Learning Studio

Conclusion
In this blog post, I’ve provided an overview of Azure Machine Learning concepts encountered in this challange module, and the solution to Challenge 1. I hope this has helped you on your own Challenge journey or provided some insight into MLOps on Microsoft Azure.
Stay tuned for part three of this blog series we’ll tackle Challange 2 and trigger our job using Github Actions.
If you are interested in joining the challenge, you can find more information and instructions on the challenge website: https://microsoftlearning.github.io/mslearn-mlops/
Happy learning and good luck! 🚀